E-Way Bill System, Rules & Generation
Under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime, an E-Way Bill, or electronic way bill, is a digital document that is necessary for the transportation of goods valued at more than ₹50,000 within India.
It guarantees openness in the flow of goods and serves as documentation of conformity with GST laws.
Registration (GST Taxpayers)
- Step 1: Begin by navigating to the official portal: ewaybillgst.gov.in.
- Step 2: Next, locate the "Registration" option and select "E-way Bill Registration" from the dropdown menu.

- Step 3: Fill in your GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) and the displayed captcha code. Click "Go" to proceed.
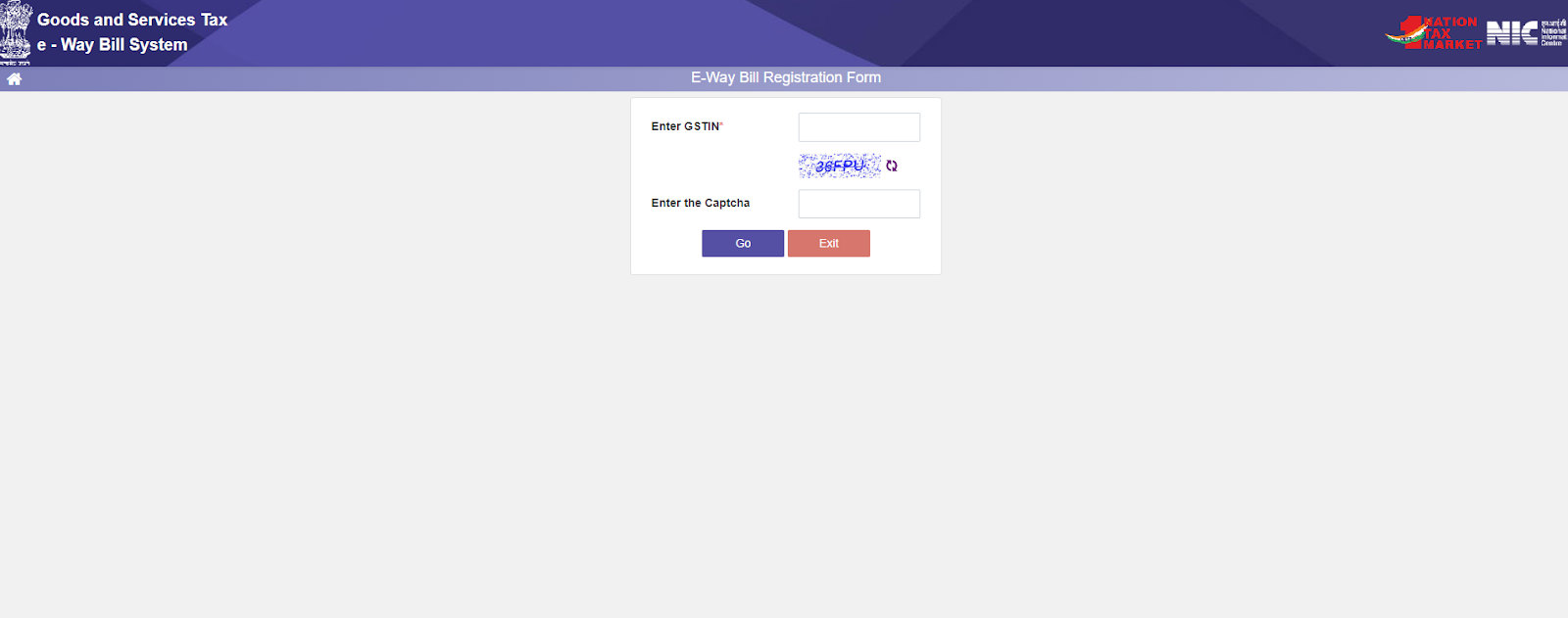
- Step 4: Verify your autopopulated details (applicant name, trade name, address, email ID, mobile number). Click "Update from GST Common Portal" if any corrections are needed. Click "Send OTP" to receive a one-time password on your registered mobile number.
- Step 5: Enter the received OTP and click "Verify OTP." Create your desired User ID (username) adhering to the 8-15 character limit, which can include alphanumeric characters and special symbols. Choose a strong password.
- Step 6: Click "Submit." Upon successful validation, your registration will be finalized, enabling you to log in with your credentials.
For Unregistered Transporters
- Step 1: The first step, visit the official portal: ewaybillgst.gov.in.
- Step 2: To initiate the enrollment, click "Registration" and select "Enrolment for Transporters."

- Step 3: Enter your PAN, legal name as per PAN, state, and trade name (if applicable). Choose the enrolment type (Regular/Bulk) and your business constitution.
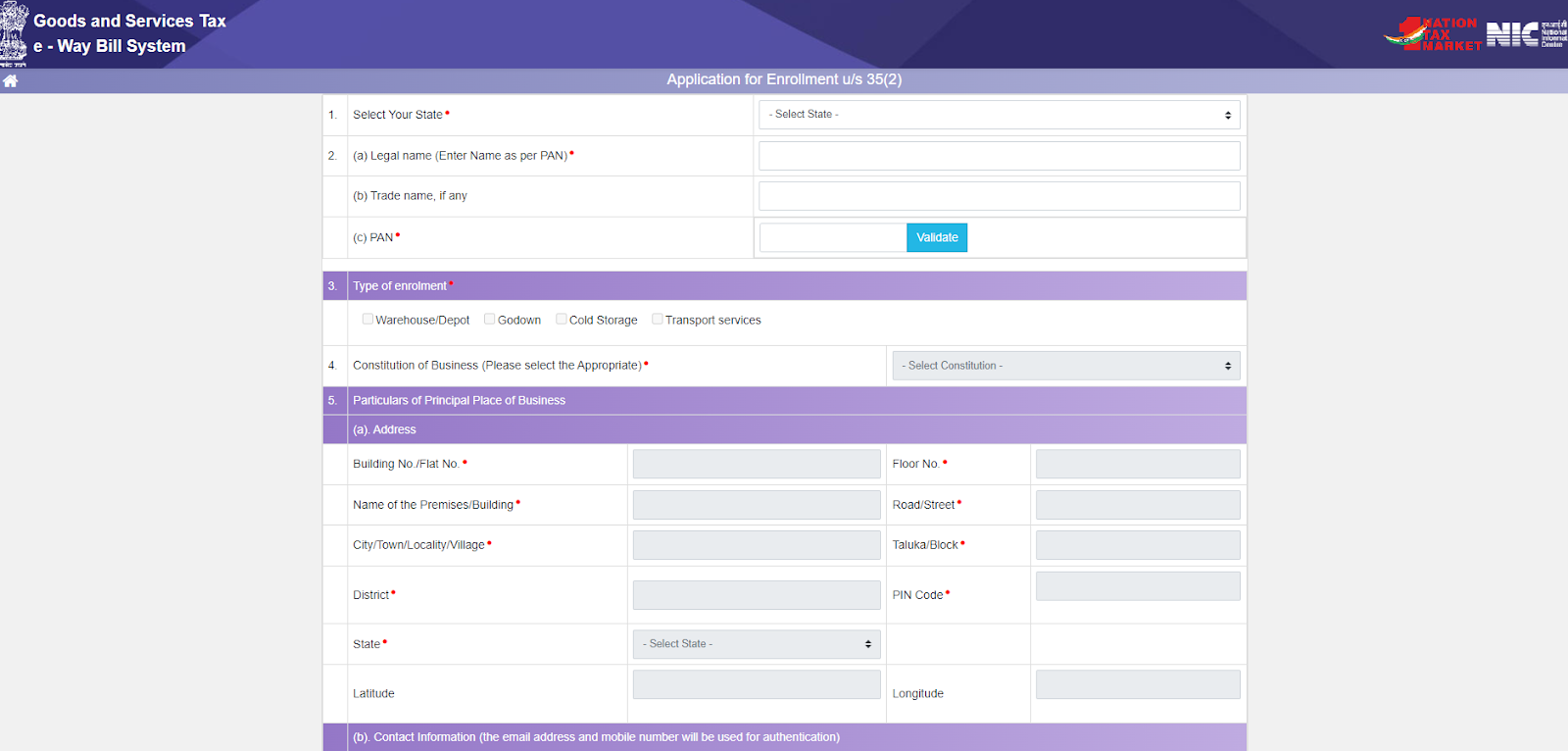
- Step 4: Now provide business address, premises type (owned/leased/rented), email ID, and mobile number.
- Step 5: Upload scanned copies of address proof (e.g., utility bill, bank statement) and identity proof (e.g., Aadhaar card, passport, voter ID). Ensure clarity and legibility.
- Step 6: Now you will be asked to create your desired User ID and a strong password, following the guidelines mentioned for registered taxpayers.
- Step 7: Check the declaration box to affirm the accuracy of provided information. Click "Submit."
- Step 8: Upon successful validation, you will receive a 15-digit Transporter ID (TRANS ID) for use in the E-Way Bill system.
Modes of generating an E-Way Bill
The E-Way Bill system provides diverse modes for generating e-Way Bills, catering to the varied needs and preferences of users.
Choosing the appropriate mode depends on factors like the frequency of transactions, technical capabilities, and accessibility to the internet.
- Web-based (Online): This is the most common and comprehensive method for generating e-Way Bills. Users can access the portal through a web browser and fill out the necessary details in Part A and Part B of the EWB-01 form.

- SMS-based: This mode is suitable for users with limited internet access or those who prefer a simpler method. After registering their mobile number on the portal, users can generate, manage, and cancel e-Way Bills by sending specific SMS codes to a designated number.
- Android App-based: The E-Way Bill mobile app, available for Android devices, offers a convenient way to generate e-Way Bills on the go. Users need to register their device's IMEI number and User ID on the portal before using the app.
- API-based: This mode is designed for businesses with advanced technical capabilities and high transaction volumes. By integrating their ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) or accounting systems with the E-Way Bill system through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), businesses can automate the E-Way Bill generation process, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
- Suvidha Provider (GSP)-based: GSPs are authorized third-party applications that offer a user-friendly interface and additional features for generating and managing E-Way Bills.
- Bulk Upload: This mode allows businesses to generate multiple e-Way Bills simultaneously by uploading an Excel template containing the relevant details of each consignment. This is a time-saving option for businesses with frequent and bulk transactions.
- Offline Tool: In areas with limited or unreliable internet connectivity, the offline tool provides a convenient way to generate e-Way Bills. Users can download the tool from the portal, fill in the details offline, and later upload the data to the portal when internet connectivity is available.
Who Should Generate the E-Way Bill?
The e-Way bill should be generated by the supplier, recipient, or transporter responsible for the movement of goods exceeding ₹50,000 in value.
| Person | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Registered Person (Supplier/Recipient) | Must generate the E-Way Bill before the movement of goods if the consignment value exceeds ₹50,000. Can voluntarily generate even if the value is less than ₹50,000. |
| Unregistered Person (Supplier) | If supplying to a registered person, the recipient must comply as if they were the supplier. |
| Transporter | Must generate the E-Way Bill if the supplier hasn't, using the information from the invoice/bill/challan. Not required if the consignments individually are ≤ ₹50,000 but collectively exceed ₹50,000. Unregistered transporters must enroll in the E-Way Bill portal to generate E-Way Bills. |
Validity
The validity of an e-way bill is determined based on the distance the goods will travel. The validity period begins from the date and time the e-way bill is generated. The specific periods are listed below:
| Type of Conveyance | Distance | Validity |
|---|---|---|
| Other than Oversized Cargo | < 200 km | 1 Day |
| Other than Oversized Cargo | Per 200 km or part | Additional 1 Day |
| Oversized Cargo | < 20 km | 1 Day |
| Oversized Cargo | Per 20 km or part | Additional 1 Day |
Additional Features and Benefits
Below are the features attached to E-Way Bill:
- QR Code: Enables quick verification.
- Custom Masters: Create lists for efficient data entry.
- Alerts and Notifications: Receive updates via online and SMS.
Its benefits include reduced paperwork, faster transit times, increased transparency, simplified compliance, and valuable data insights for businesses and the government.
Additionally, the system integrates with RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology to enable seamless tracking of goods movement.
Purpose
The E-Way Bill system replaces numerous state-specific waybills with a single electronic system, in line with the GST thought of "One Nation-One Tax-One Market". Businesses can comply more easily as a result, and interstate trade inside India is made easier.
E-Way Bills are required for the interstate transportation of products valued at more than ₹50,000 when they are delivered by motor vehicle.
Nonetheless, in certain situations, an e-Way Bill is not necessary, even if the amount above ₹50,000:
- Goods transported using non-motorized vehicles.
- Goods transported from or to airports, customs ports, air cargo complexes, and land customs stations.
- Goods transported under customs supervision or seal.
- Transit cargo to or from Nepal or Bhutan.
- Empty cargo containers.
- Goods transported by rail where the consignor is the Central Government, State Governments, or local authorities.
Threshold Limits for Intrastate Movement of Goods
Below is a list of the e-way bill threshold limits for intrastate movement of goods in each state.
| Sr. No. | State | E-Way Bill Threshold Limit | Relevant Notification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | CCTs Ref. in CCW/GST/74/2015, dated 11th April 2018 |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | CBIC Press Release dated 23-04-2018 and Notification No. 14/2018- State Tax dated 23rd March 2018 |
| 3 | Assam | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 30/2019-GST, dated 16th December 2019; Notification No. 07, dated 7th May 2018 |
| 4 | Bihar | Above Rs. 1,00,000 | Notification No. S.O. 14, dated 14th January 2019 |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Rs. 50,000 for specified goods | Notification No. F-10-31/2018/CT/V (46), dated 19th June 2018 |
| 6 | Delhi | Rs. 1,00,000 | Notification No. 03, dated 15th June 2018 |
| 7 | Goa | Rs. 50,000 for specified 22 goods | Notification No. CCT/26-2/2018-19/36, dated 28th May 2018 |
| 8 | Gujarat | No e-way bill required for goods other than specified classes | No.GSL/GST/RULE-138(14)/B.19, dated 19th September 2018 |
| 9 | Haryana | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 49/ST-2, dated 19th April 2018 |
| 10 | Himachal Pradesh | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 12-4/78-EXN-TAX-17408, dated 31st May 2018 |
| 11 | Jammu and Kashmir | No e-way bill required | Notification No. 64, dated 30th November 2019 |
| 12 | Jharkhand | Above Rs. 1,00,000 for goods other than specified goods | Notification No. S.O. 66, dated 26th September 2018 |
| 13 | Karnataka | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Press Release, dated 29-03-2018 and Notification No. FD 47 CSL 2017 dated 23rd March 2018 |
| 14 | Kerala | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Press Release dated 10th April 2018 |
| 15 | Madhya Pradesh | Rs. 50,000 for specified 11 goods | Notification No. F-A 3-08-2018-1-V(43), dated 24th April 2018 |
| 16 | Maharashtra | Rs. 1,00,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 15E, dated 29th June 2018 |
| 17 | Manipur | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | CBIC Press Release dated 24th May 2018 |
| 18 | Meghalaya | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. ERTS (T) 84/2017/20, dated 20th April 2018 |
| 19 | Mizoram | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No.J.21011/2(iii)/2018-TAX/Pt, dated 2nd July 2018 |
| 20 | Nagaland | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 6/2018. Dated: 19th April 2018 |
| 21 | Odisha | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Press Release dated 31st May 2018 |
| 22 | Puducherry | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. F. No. 3240/CTD/GST/2018/3, dated 24th April 2018 |
| 23 | Punjab | Rs. 1,00,000 for all taxable goods | No. PA/ETC/2018/175, dated 13th September 2018 |
| 24 | Rajasthan | Rs. 1,00,000 for all taxable goods except specified items | Notification No. F.17(131- Pt.-II) ACCT/GST/2017/6672, dated 30.03.2021; Notification No. F17 (131) ACCT/ GST/2017/3743, dated 6th August 2018 |
| 25 | Sikkim | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Press Release dated 23rd April 2018 |
| 26 | Tamil Nadu | Rs. 1,00,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 09, dated 31st May 2018 |
| 27 | Telangana | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Press Release dated 10th April 2018 |
| 28 | Tripura | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No.F.1-11(91)-TAX/GST/2018 (Part- I), dated 17th April 2018 |
| 29 | Uttar Pradesh | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 38, dated 11th April 2018; Notification No.-E-way bill- R.F.I.D./sachaldal/2018-19/1025/commercial tax, dated 7th September 2018 |
| 30 | Uttarakhand | Rs. 50,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 239/CSTUK/GST-Vidhi/2018-19, dated 17th April 2018 |
| 31 | West Bengal | Rs. 1,00,000 for all taxable goods | Notification No. 11/2018-C.T./GST, dated 30th May 2018; Notification No. 13, dated 6th June 2018 |