PMAY-G Beneficiary List
The Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Gramin (PMAY-G) aims to provide affordable housing to the rural poor. Launched as a part of the broader Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana. The scheme aims specifically at enhancing the living conditions in rural India by providing pucca houses to those living in dilapidated or kutcha houses.
This guide offers an overview on how to check the PMAY-G beneficiary list, ensuring easy verification of eligibility and status through the PMAYG.niC.iN and rhReporting portals.
Check PM Awas Gramin List 2024
To check the PM Awas Gramin List, follow these instructions:
- Go to the official site: pmayg.nic.in.
- Select "Awaassoft" from the menu.
- Choose "Report" from the dropdown that appears.
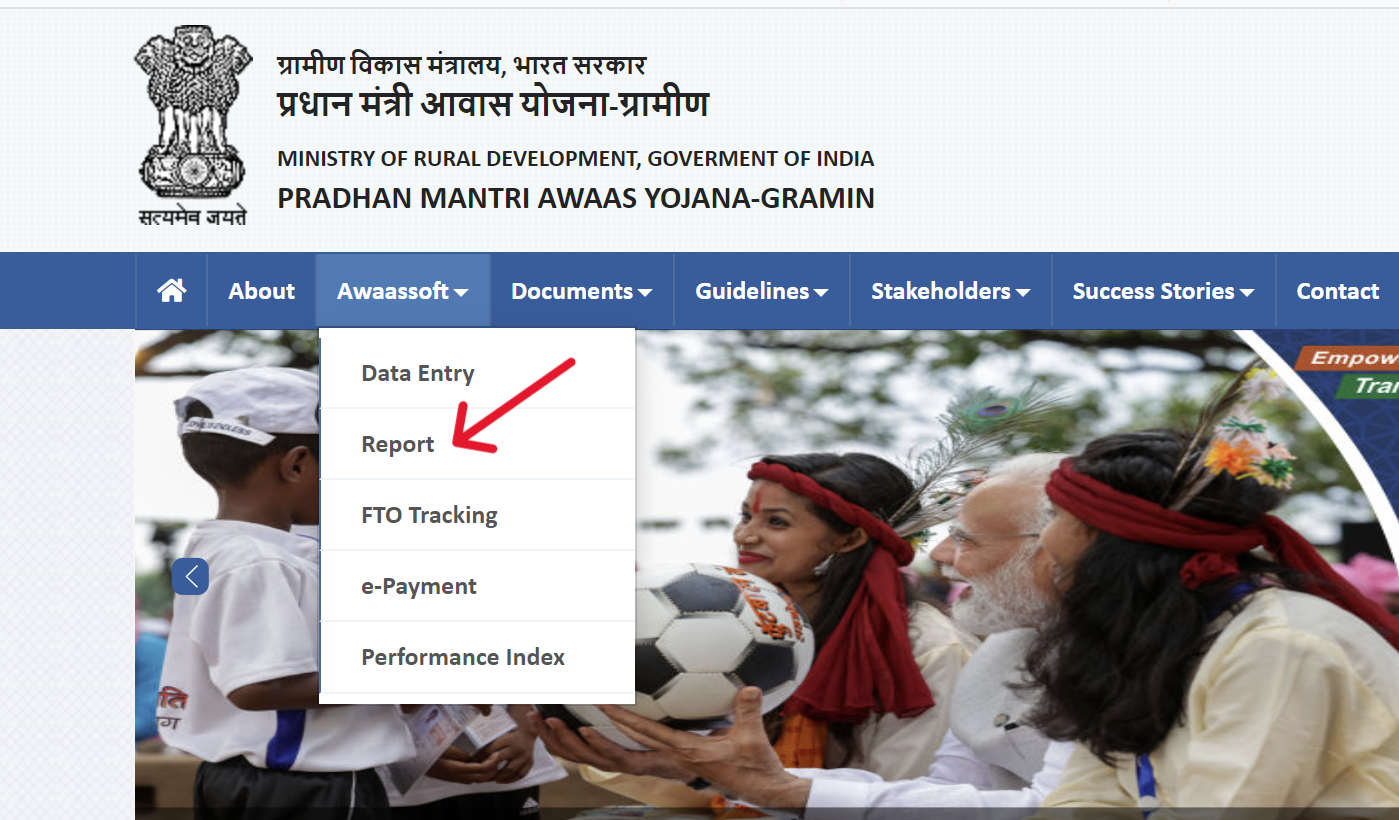
- You'll be taken to rhReporting.nic.in Portal.
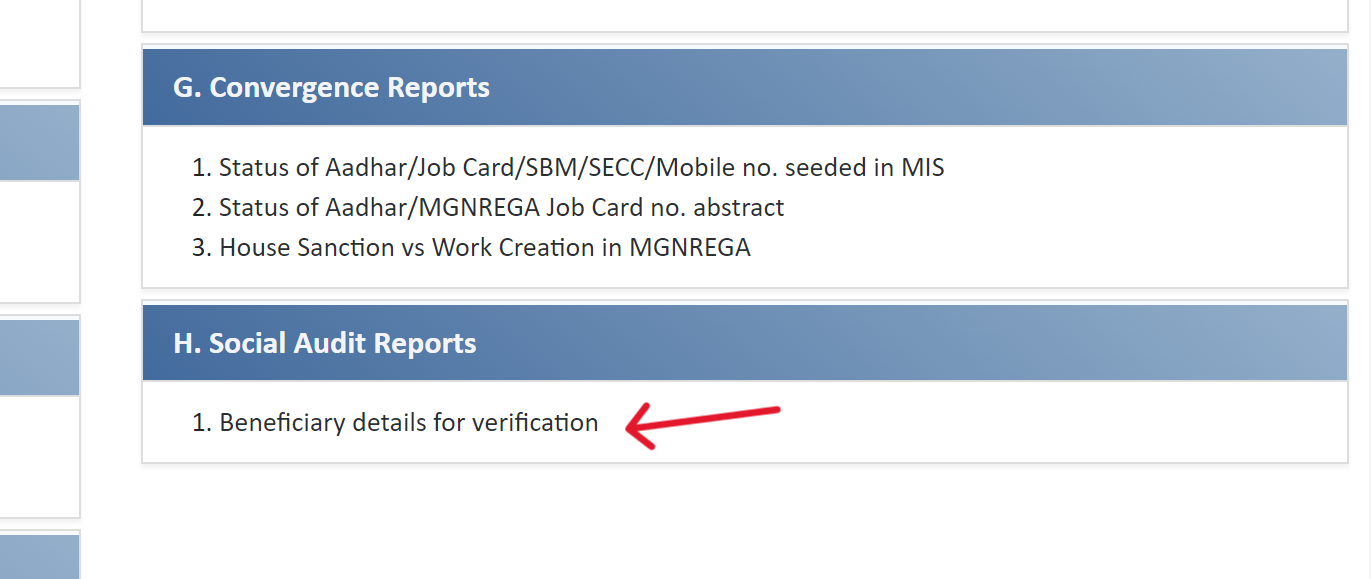
- Under "Social Audit Reports," find and click on "Beneficiary details for verification."
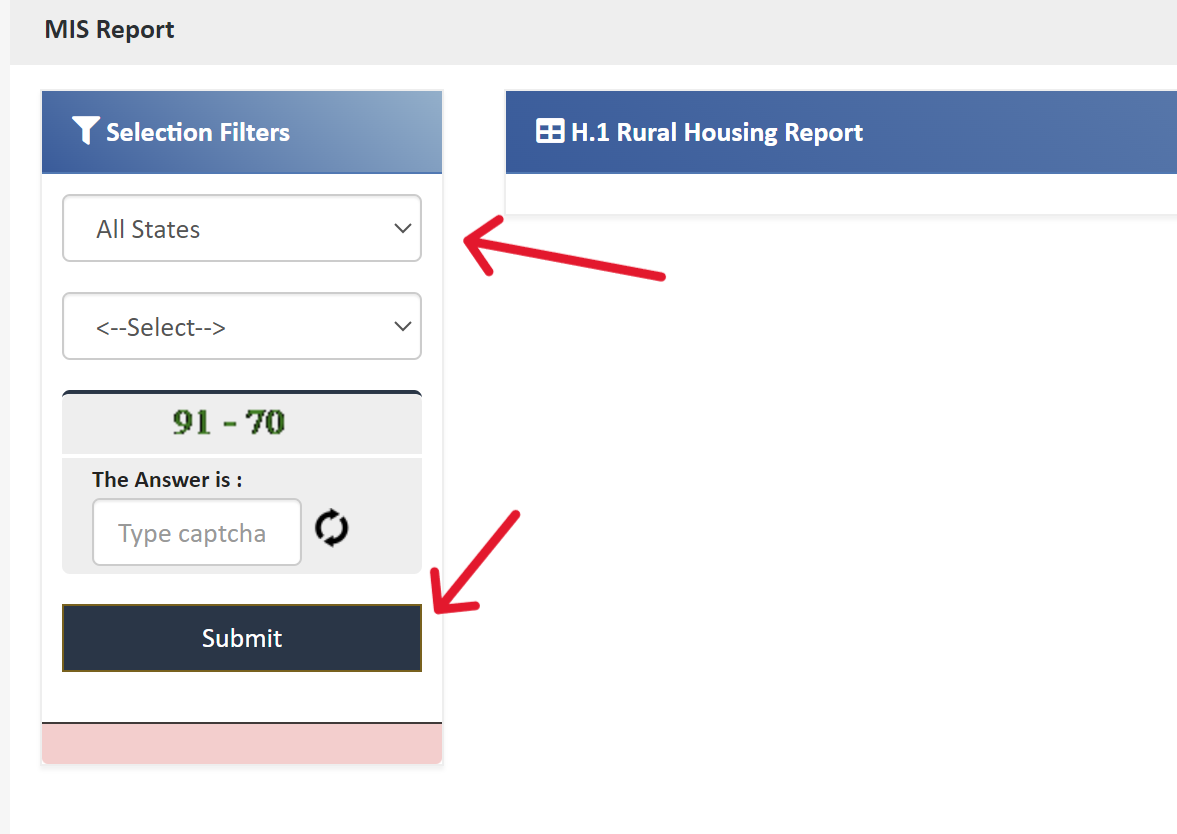
- On the MIS Report page, fill in the necessary fields like state, district, block, and village.
Hit "Submit" to access or check the beneficiary list.
State-Wise Beneficiary List
To check the state-wise Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awas Yojana list for 2024, click on a state link below, select your district, block, and village, enter the captcha, and click the submit button.
Beneficiary Selection under PMAY-G
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana - Gramin (PMAY-G) is a government initiative aimed at providing affordable pucca houses with basic amenities to rural houseless families and those living in kutcha houses by 2024.
Key Facts About Beneficiaries
Below are the Key Facts About Beneficiaries:
Identification of Beneficiaries:
- Beneficiaries under PMAY-G are identified using data from the Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 2011, which assesses housing deprivation across rural India.
- The eligible beneficiaries include houseless families and those living in kutcha houses with walls and roofs made from non-durable materials like mud, grass, or bamboo.
- The Gram Sabha (village council) plays a key role in verifying and finalizing the list of eligible beneficiaries to ensure transparency and fairness.
Prioritization Criteria:
- The scheme prioritizes beneficiaries based on the severity of their housing deprivation. Houseless families and those living in one or two-room kutcha houses are given the highest priority.
- Specific social categories such as Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), minorities, and female-headed households receive additional focus.
- Households meeting the “automatically included” criteria, such as those with no able-bodied adults, widows, or disabled family members, are given priority to receive housing assistance.
Loan Facility:
- In addition to the financial assistance provided by the government, beneficiaries can also access loans up to ₹70,000 to supplement the construction costs of their houses.
- The loan facilitation process is managed through the State Level Bankers’ Committee (SLBC) and District Level Bankers’ Committee (DLBC) to ensure ease of access for beneficiaries.
Support for Vulnerable Groups:
- PMAY-G includes special provisions for persons with disabilities, widows, and elderly beneficiaries. These households are given additional priority during the beneficiary selection process.
- The program aims to ensure that 5% of beneficiaries are from households with persons with disabilities, with special focus on women with benchmark disabilities.
House Ownership and Gender Empowerment:
- One of the notable features of PMAY-G is the emphasis on female ownership. Houses are typically sanctioned in the name of the female head of the household, or jointly in the name of both the husband and wife.
- This initiative is designed to promote gender equity and ensure that women in rural areas gain property ownership and security.
Technical and Financial Support:
- Beneficiaries are provided with both technical and financial assistance to construct houses. They receive unit assistance of ₹1.20 lakh in plains and ₹1.30 lakh in hilly or difficult areas for house construction.
- The financial assistance is provided in three or more installments linked to the construction progress, and all payments are made through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) directly into the beneficiaries' bank accounts to avoid delays and corruption.
Benefits
- Financial Assistance for Housing: Eligible beneficiaries receive financial aid to construct or upgrade their houses. The scheme provides ₹1.20 lakh for plain areas and ₹1.30 lakh for hilly, difficult, and Integrated Action Plan (IAP) areas.
- Focus on Rural Areas: The scheme targets rural populations, ensuring that those in need have access to adequate housing facilities.
- Basic Amenities: Houses built under PMAY-G come with essential amenities such as a hygienic cooking space, electricity connection, and a toilet facility, enhancing the overall living standards.
- Sustainable Construction: The scheme encourages the use of eco-friendly and sustainable building materials and techniques, promoting environmentally conscious housing solutions.
- Employment Opportunities: Construction activities under PMAY-G generate local employment opportunities, boosting the rural economy.
- Women Empowerment: The scheme promotes women’s empowerment by mandating that the house should be registered in the name of the female head of the household or jointly in the name of both spouses.
- Enhanced Livelihood: By providing secure and stable housing, PMAY-G helps improve the overall livelihood of beneficiaries, contributing to poverty alleviation and social well-being.